
What Is Fiber Optic Cable?
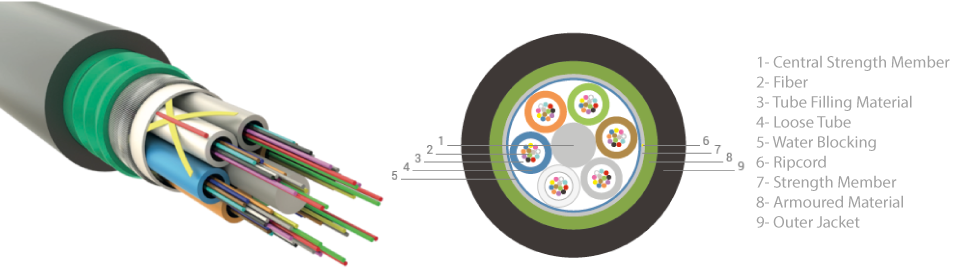
Fiber optic cables are made up of thin strands of glass or plastic, known as optical fibers, which are encased in a protective jacket. These strands are extremely thin, with a diameter of just a few hundred micrometers.
Light signals are transmitted through the optical fibers using a process called total internal reflection. When light is shone into the fiber, it bounces off the walls of the fiber at a specific angle, called the critical angle. This allows the light to travel along the fiber without being absorbed or scattered.
Optical fibers are made of a highly transparent material called silica, which has a very low refractive index. This allows the light to travel through the fiber with minimal loss of signal strength, making it possible to transmit data over long distances.
Fiber optic cables are typically used for telecommunications, internet connectivity, and data transmission. They are also used in audio and video systems, medical equipment, military communications systems, and other specialized applications.
One of the main advantages of fiber optic technology is its high bandwidth, which allows it to transmit large amounts of data at high speeds. It is also immune to electromagnetic interference, making it a reliable choice for transmitting data over long distances.
In addition, fiber optic cables are lighter and thinner than traditional copper wires, making them easier to install and handle. They are also more resistant to signal degradation, making them a more reliable choice for transmitting data over long distances.
Overall, fiber optic technology has revolutionized the way we transmit and receive data, and will continue to play a crucial role in the development of modern communication systems.

Fiber Optic Cable Types and Applications
There are several types of fiber optic cables, each designed for specific applications. The main types of fiber optic cables include:
- Single mode fiber optic cable: This type of fiber optic cable is made up of a single strand of glass or plastic fiber, and is used for transmitting data over long distances. It is typically used in telecommunications, data centers and internet connectivity.
- Multi-mode fiber optic cable: This type of fiber optic cable is made up of multiple strands of glass or plastic fiber, and is used for transmitting data over shorter distances. It is typically used in local area networks (LANs), data centers, audio and video systems.
- Plastic optical fiber (POF): This type of fiber optic cable is made from plastic rather than glass, and is used for transmitting data over shorter distances. It is typically used in consumer electronics and automotive applications.
Fiber optic cables have a number of applications, including telecommunications, internet connectivity, audio and video transmission, and medical imaging. They are also used in military and defense systems, as well as in construction for structural monitoring and lighting.
Fiber Optic Cable and Energy Efficiency
Fiber optic cables are generally considered to be more energy efficient than other types of communication cables, such as copper wire. This is because fiber optic cables are able to transmit data over longer distances with less signal loss, which means that they require less energy to operate.
There are several applications where fiber optic cables can help to improve energy efficiency:
Data Centers: Fiber optic cables are often used to connect data centers, which are large facilities that house servers and other computing equipment. By using fiber optic cables instead of copper wires, data centers can reduce their energy consumption and lower their carbon footprint.
Smart Grid: The "smart grid" refers to the modernized version of the electrical grid that is designed to be more efficient and reliable. Fiber optic cables are used to transmit data between different parts of the smart grid, helping to improve energy efficiency and reduce waste.
Building Automation: Fiber optic cables are often used in building automation systems, which are used to control and monitor various systems within a building. By using fiber optic cables, buildings can reduce their energy consumption and improve their overall efficiency.
Industrial Applications: Fiber optic cables are also used in industrial applications, such as manufacturing and oil and gas exploration. By using fiber optic cables, these industries can reduce their energy consumption and improve their overall efficiency.
Overall, fiber optic cables offer a number of benefits in terms of energy efficiency, and they are being used in an increasingly wide range of applications to help reduce energy consumption and improve efficiency.
Fiber Optic Applications in Military and Defense
Fiber optic cables are used in a variety of military and defense applications due to their high speeds, reliability, and security. Here are some examples of how fiber optic cables are used in military and defense:
Military Communication: Fiber optic cables are used to transmit data for military communication systems, including voice, video, and data. They are particularly well-suited for use in military communication systems due to their high speeds, long distance capabilities, and resistance to interference.
Military Surveillance: Fiber optic cables are also used in military surveillance systems, such as those used to monitor borders and other areas of interest. They can transmit high-definition video and other data over long distances, making them ideal for use in surveillance applications.
Military Vehicles: Fiber optic cables are used in military vehicles such as tanks and airplanes to transmit data for various systems, including communication, navigation, and weapons systems.
Military Satellites: Fiber optic cables are used in military satellites to transmit data back to earth. They are able to transmit data at high speeds over long distances, making them ideal for use in satellite communication systems.
Overall, fiber optic cables play a key role in military and defense applications due to their high speeds, reliability, and security. They are used in a variety of systems to transmit data for communication, surveillance, and other purposes.





